🐬 Dolphain
"So long, and thanks for all the fish data"
A Python toolkit for analyzing underwater acoustic recordings and understanding dolphin communication patterns
Where Marine Biology meets Signal Processing, AI, and Physics
What is Dolphain?
Dolphain is a scientifically rigorous Python package for analyzing underwater acoustic recordings from the Gulf of Mexico. Our mission: decode dolphin communication patterns through clicks and whistles.
Learn more about data sources and attributions →
We're working with EARS (Ecological Acoustic Recorder) data sampled at 192 kHz, perfect for capturing the 2-20 kHz range where dolphins communicate with each other.
See It In Action
Real outputs from analyzing Gulf of Mexico underwater recordings. All visualizations generated from actual EARS data files.
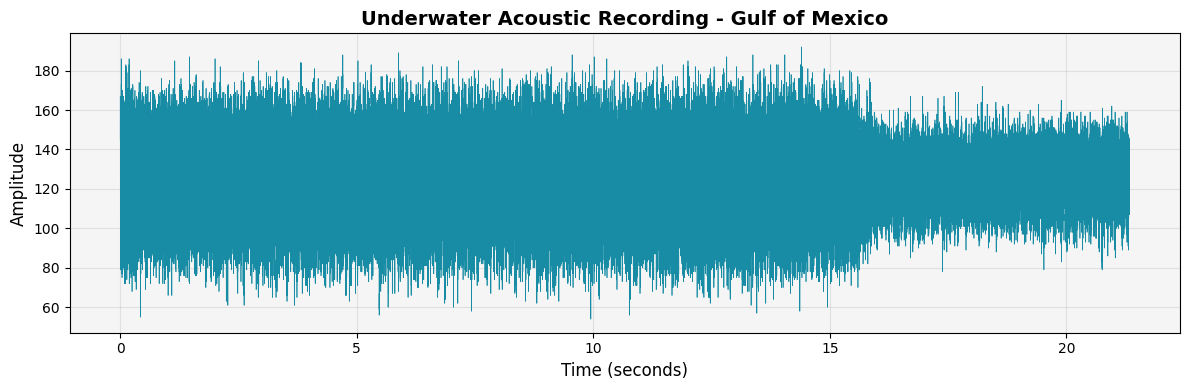
📈 Waveform Analysis
Time-domain visualization of a 21-second underwater recording. Each peak represents acoustic energy from marine life, boats, or environmental noise.
import dolphain data =
dolphain.read_ears_file('recording.210')
# Plot the waveform
dolphain.plot_waveform(data)
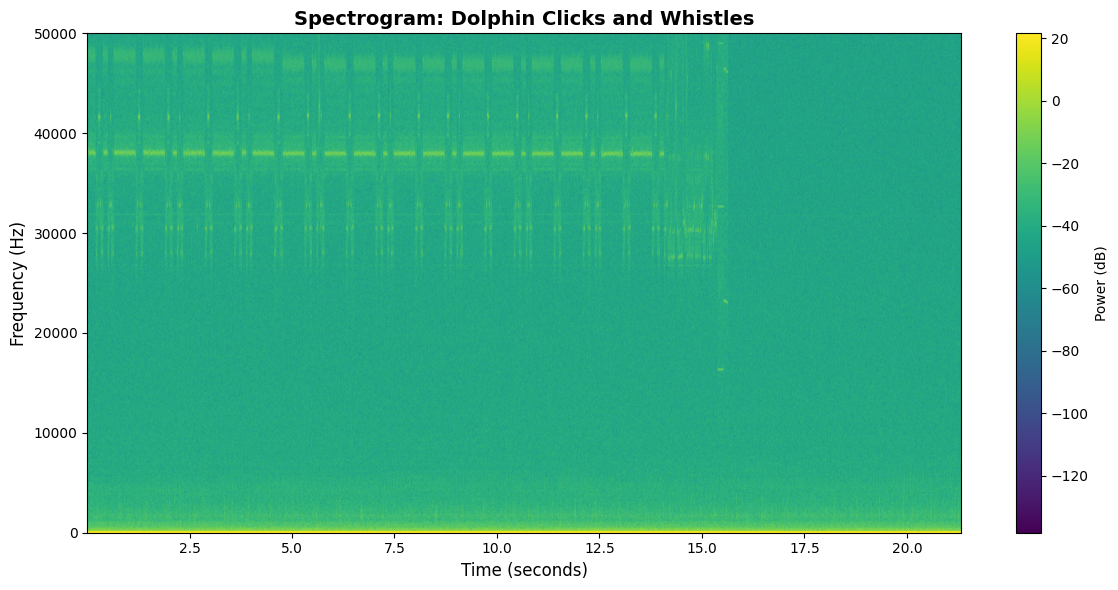
🎨 Spectrogram Visualization
Frequency-time representation showing where dolphin communication happens. Whistles appear as contours in the 2-20 kHz range, while clicks show up as vertical lines at higher frequencies.
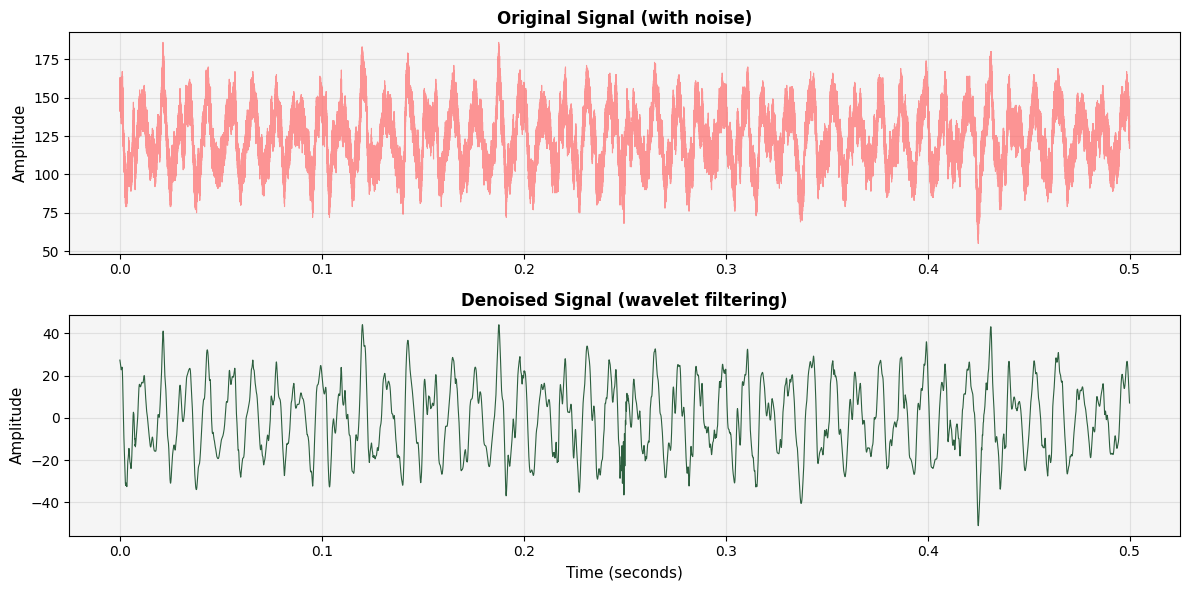
🌊 Wavelet Denoising
Before and after comparison showing how wavelet filtering removes background noise while preserving dolphin vocalizations. The denoised signal reveals clearer transient features for click detection.
# Clean the signal
denoised = dolphain.wavelet_denoise(data['data'])
# Compare results
dolphain.plot_denoising_comparison(data['data'], denoised,
data['fs'])
718587E0.210 recorded in the Gulf of Mexico as
part of the LADC-GEMM marine mammal monitoring project. Duration:
21.33 seconds, Sample rate: 192 kHz.
Features
Cutting-edge acoustic analysis tools powered by advanced signal processing
Unique Signal Detection
NEW! Multi-band spectral analysis identifies exceptional acoustic features: harmonics, fast frequency sweeps, simultaneous signals, and spectral complexity. Automatically scores and ranks the most unique recordings.
Conservative Click & Chirp Detection
Ultra-precise detection of dolphin echolocation clicks and communication chirps. Uses 99.5th percentile thresholding, regularity analysis, and sharp peak detection to minimize false positives.
EARS File I/O
Read and process EARS binary format (.130, .190, .210) with full metadata extraction.
Signal Processing
Wavelet-based denoising using VisuShrink thresholding for clean acoustic data.
Visualization
Beautiful spectrograms, waveforms, and comparative analysis plots with interactive audio players.
Batch Processing
Process hundreds of files with progress tracking, checkpointing, and error handling.
Automated Analysis Pipeline
Choose from standard detection (chirps & clicks) or unique signal mode. Resumable processing with checkpoint system.
Interactive Showcase
Web-based gallery with synchronized waveform/spectrogram playback and audio controls. Explore the most interesting recordings.
Branch Explorer
Follow curated pods by energy, harmony, and flow in our interactive Branch Explorer.
🚀 Latest Enhancement: Dual-Mode Detection System
📍 Standard Mode
Conservative detection of chirps (frequency sweeps >3kHz, 0.3s+) and click trains (15+ clicks, ultra-regular spacing).
python scripts/quick_find.py --mode standard
✨ Unique Mode
Hunt for exceptional features: multi-band activity, harmonic structures, ultra-fast sweeps, burst clicks, spectral complexity.
python scripts/quick_find.py --mode unique
Both modes output compatible results for the showcase generator. Choose based on your research goals!
Get Started
🚀 Instant Start: No Installation Required
Jump straight into analysis with Dolphain Studio. Run real Python code in your browser, powered by Pyodide (WASM).
💻 Launch StudioPerfect for learning the basics of signal processing and dolphin acoustics.
Local Installation (for Developers)
# Clone the repository git clone
https://github.com/micha2718l/dolphain.git cd dolphain # Create
virtual environment python3 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate
# On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate # Install in development mode
pip install -e .
Basic Usage
import dolphain
# Read an EARS file
data = dolphain.read_ears_file('data/recording.210')
# Create a quick overview plot
dolphain.plot_overview(data, fmax=50000)
# Denoise the signal
denoised = dolphain.wavelet_denoise(data['data'])
# View the difference
dolphain.plot_denoising_comparison(data['data'], denoised,
data['fs'])
The Science of Dolphin Communication
Two Types of Sounds
Clicks (Echolocation)
Purpose: Navigation and hunting
Frequency: >110 kHz, peaks >220 kHz
Duration: Microseconds to milliseconds
Pattern: Rapid trains ending in "terminal buzz" (200+ clicks/sec)
Whistles (Communication)
Purpose: Social interaction
Frequency: 2-20 kHz
Duration: 0.5-1.5 seconds
Types: Signature whistles (individual "names"), pulsed calls
Current Research
We're analyzing 100+ underwater recordings from the Gulf of Mexico, developing algorithms to automatically detect and classify dolphin vocalizations.
Research Context
This work builds upon the LADC-GEMM project's extensive acoustic monitoring infrastructure. The consortium deployed autonomous underwater gliders, research vessels, and bottom-mounted EARS recorders throughout the Gulf to assess marine mammal populations and ambient noise levels following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
Achievements
- ✅ Core Library: Stable and production-ready
- ✅ Click Detection: Teager-Kaiser energy operator with threshold tuning
- ✅ Batch Framework: Process hundreds of files efficiently
- ✅ Runtime Guardrails: Safe, memory-efficient processing
- ⏳ Whistle Detection: In development
- ⏳ Signature Matching: Future work
Ready to contribute? Jump to our Contribution Guide below to join the vibe coding revolution! 🚀
🌊 Join the Vibe Coding Revolution 🐬
This entire project was built through "vibe coding" - a collaborative approach where human intuition meets AI capabilities. You don't need to be an expert. You just need curiosity, good vibes, and a willingness to explore! 🎨✨
The more human brains + LLM brains we get working together, the better. Let's decode dolphin communication as a team! 🧠🤖🐬
🌊 Join the Mission
Dolphain is more than code—it's a convergence of disciplines. Whether you're a physicist, a biologist, or a coder, your skills can unlock the secrets of the ocean.
For Biologists
Help us validate our detections. Are we finding clicks or shrimp noise? Use the Showcase to listen and label. Your expertise grounds our algorithms in reality.
For Physicists
Underwater acoustics is complex physics. Help us improve our wave propagation models, refine our denoising algorithms, and understand the spectral properties of the Gulf.
For AI Engineers
We're building the "Rosetta Stone" of dolphin communication. Help us train models to classify whistles, cluster similar signals, and detect patterns in the noise.
For Developers
Build tools that make science accessible. Improve the Studio, optimize our batch processing pipeline, or create new visualizations for the Branch Explorer.
🎯 Our Philosophy
Human + AI Collaboration
Combine your creative vision with AI's technical execution. You guide, AI builds.
Document Everything
Keep notes, update docs, track decisions. Future you (and others) will thank you!
Plan for Context Loss
Sessions end, windows close. Design your work to be resumable by anyone.
Vibe First, Perfect Later
Get ideas flowing, iterate quickly, refine as you go. Progress > Perfection.
🚀 Quick Start: Your First Contribution
Fork & Clone
Create your own copy of the repository. You'll work here safely without affecting the main project.
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/dolphain.git
cd dolphain
git remote add upstream https://github.com/micha2718l/dolphain.git⚠️ Important: You cannot push directly to main. This is intentional! It keeps the project safe and encourages good collaboration practices.
Create a Branch
Always work on a feature branch. Name it something descriptive.
git checkout -b feature/whistle-detection
# or
git checkout -b docs/improve-readme
# or
git checkout -b fix/batch-processing-bug💡 Tip: Use prefixes like feature/, docs/, fix/, experiment/ to keep things organized.
Set Up Your Environment
Get Python and dependencies installed. Use the AI to help you!
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
# Install in editable mode
pip install -e .
# Install dev dependencies if you're adding tests
pip install pytest matplotlib numpy scipy🤖 Pro Tip: Ask your AI assistant: "Help me set up the Dolphain development environment"
Read the Context
Before diving in, understand where we are. These docs are your map!
- CONTINUATION_GUIDE.md - Comprehensive overview & next steps
- PROJECT_STATUS.md - Current state of the project
- README.md - Installation & basic usage
- SESSION_STATE.md - Latest session notes
📖 Why? These docs minimize lost time when context windows clear or collaborators switch.
Pick Your Adventure
What sounds fun to you? Choose based on your interests!
🎨 Creative Track
Build tools like the Dolphin Composer, make visualizations, have fun!
Get Inspired →Vibe Code with Your AI
Here's where the magic happens! Partner with an LLM to build.
🌟 Remember: You're the creative director. The AI is your implementation partner.
Commit Often, Document Always
Make small, frequent commits with clear messages.
git add dolphain/signal.py
git commit -m "Add whistle detection using spectrogram peaks
- Implement peak finding with scipy
- Add frequency range filtering (2-20 kHz)
- Include docstrings and type hints
- Add basic unit tests"
git push origin feature/whistle-detection💎 Good commits: Explain WHAT and WHY, not just WHAT. Future readers will love you!
Update the Docs
Before you finish, update relevant documentation.
- Add your feature to
README.md -
Update
PROJECT_STATUS.mdwith what's complete -
Create or update
SESSION_STATE.mdwith your progress -
If you finished a big feature, add a new doc file (like
WHISTLE_DETECTION.md)
📚 Why? Documentation is a gift to the next contributor (who might be you in 3 months!).
Create a Pull Request
Share your work! Go to GitHub and open a PR.
PR Template to use:
## What This PR Does
Brief description of the feature/fix
## Changes Made
- List of specific changes
- Be clear and concise
## Testing
How you tested this (manual tests, unit tests, etc.)
## Documentation Updated
- [ ] README.md
- [ ] PROJECT_STATUS.md
- [ ] Relevant guide docs
- [ ] Inline code comments
## Notes for Reviewer
Anything special to know? Any decisions you made?
## AI Collaboration Notes
Which AI you used, what worked well, any challenges?🎉 Celebrate: You just contributed to dolphin communication research!
🏆 Best Practices for Vibe Coding
📝 Session Notes Are Sacred
Start every session with: "Let's create a SESSION_NOTES.md to track what we do today." This helps when you resume later or hand off to another contributor.
See Example Session Notes
# Session Notes - 2025-10-11
## Goal
Implement basic whistle detection using spectrogram analysis
## Context
- Read CONTINUATION_GUIDE.md
- Whistle detection is marked as "In Development"
- Need to work in dolphain/signal.py
## Progress
- [x] Implemented spectrogram generation
- [x] Added peak detection for whistle candidates
- [x] Created unit tests
- [ ] Need to add frequency filtering
- [ ] Need to test on real EARS data
## Next Steps
1. Add frequency range filtering (2-20 kHz)
2. Test on multiple EARS files
3. Document the approach
4. Update PROJECT_STATUS.md
## AI Used: GitHub Copilot
## Issues Encountered: None major
## Time: ~2 hours🎯 One Feature Per Branch
Resist the temptation to fix "just one more thing." Keep branches focused. It makes reviews easier and reduces merge conflicts.
🧪 Test Your Code
Ask your AI to write tests! Even simple tests catch bugs and show future contributors how your code works.
pytest tests/
# Make sure existing tests still pass!💬 Over-Communicate
In PRs, commits, and docs - explain your thinking. What seemed obvious today will be mysterious in 6 months.
🔄 Sync Regularly
Pull changes from upstream often to avoid nasty merge conflicts.
git fetch upstream
git merge upstream/main
# Fix any conflicts locally🎨 Embrace Iteration
First version doesn't need to be perfect. Get it working, get feedback, improve. That's the vibe coding way!
📚 Essential Resources
🗺️ Project Documentation
- Continuation Guide - Start here!
- Project Status - What's done
- README - Installation & usage
- Data Attribution - Data sources
🔬 Scientific Background
- LADC-GEMM - Data source
- GoMRI - Funding organization
- Marine Mammal Sounds - Educational resource
💻 Technical Resources
🤖 AI Collaboration
- GitHub Copilot - AI pair programmer
- Claude, ChatGPT, or your preferred LLM
- Cursor, Cody, or AI-enhanced IDEs
❓ Common Questions
I'm not a dolphin expert. Can I still contribute?
Absolutely! Some of the best contributions come from fresh perspectives. Focus on code quality, documentation, testing, or tooling. The scientific knowledge can be learned along the way!
I've never used AI to code before. Is that okay?
Perfect! This project is a great place to learn. Start small: ask your AI to explain existing code, help write tests, or improve documentation. Build confidence gradually!
What if I get stuck or context windows out?
That's expected! That's why we emphasize documentation. Check SESSION_STATE.md, ask the maintainer (Michael) for guidance, or create a GitHub issue explaining where you got stuck. The community is here to help!
How do I know what to work on?
Check the issues! Look for "good first issue" or "help wanted" tags. Or read CONTINUATION_GUIDE.md and pick something that sounds interesting. When in doubt, ask in a GitHub issue!
Can I just experiment without a clear goal?
Yes! Create an
experiment/your-idea branch and explore. Document
what you learn. Some of the best features started as experiments!
What if my PR doesn't get merged?
That's okay! You still learned something valuable. PRs might not merge because of timing, scope, or direction changes. Feedback helps everyone improve!
Ready to Dive In? 🌊
The dolphins are waiting for you to help decode their language! Pick a path, grab your AI buddy, and let's vibe code together! 🐬✨
Dive In
Ready to help decode dolphin communication?
🐬 Explore the Showcase
Listen to the most interesting dolphin vocalizations from the Gulf of Mexico with interactive audio and synchronized spectrograms.
🎵 Open Showcase🎨 Try the Dolphin Composer
Create your own dolphin-like sounds with our interactive synthesizer. Experiment with frequencies, patterns, and effects!
🎹 Launch Composer🌿 Explore Branch Patterns
Navigate curated pods organized by energy, harmony, and flow in our interactive branch explorer.
🌳 Browse Branches